In the first part, we looked at the most important building blocks and strategies for creating a product vision. Today, we would like to focus on how to work with a product vision and where it can best be integrated into agile software development.
The product vision not only serves as a guideline for the development of a product, but also plays an important role in various phases of the product life cycle - if used correctly. From the definition of the product strategy to the operational development of the product, the vision can serve as a point of orientation. It ensures that all activities are geared towards realising the vision.
A key aspect of working with a product vision is the regular review of whether the vision has already been fulfilled or whether adjustments still need to be made. Key figures can be derived from the vision in order to measure progress and the success or added value for the product's users.
Examples of key figures:
- Number of users of the product
- User satisfaction
- Quantifiable added value offered by the product
By regularly measuring and analysing the key figures, the development team can better understand how well the vision is being implemented and which areas may need to be improved. Overall, working with a product vision enables a targeted and strategic direction for product development.
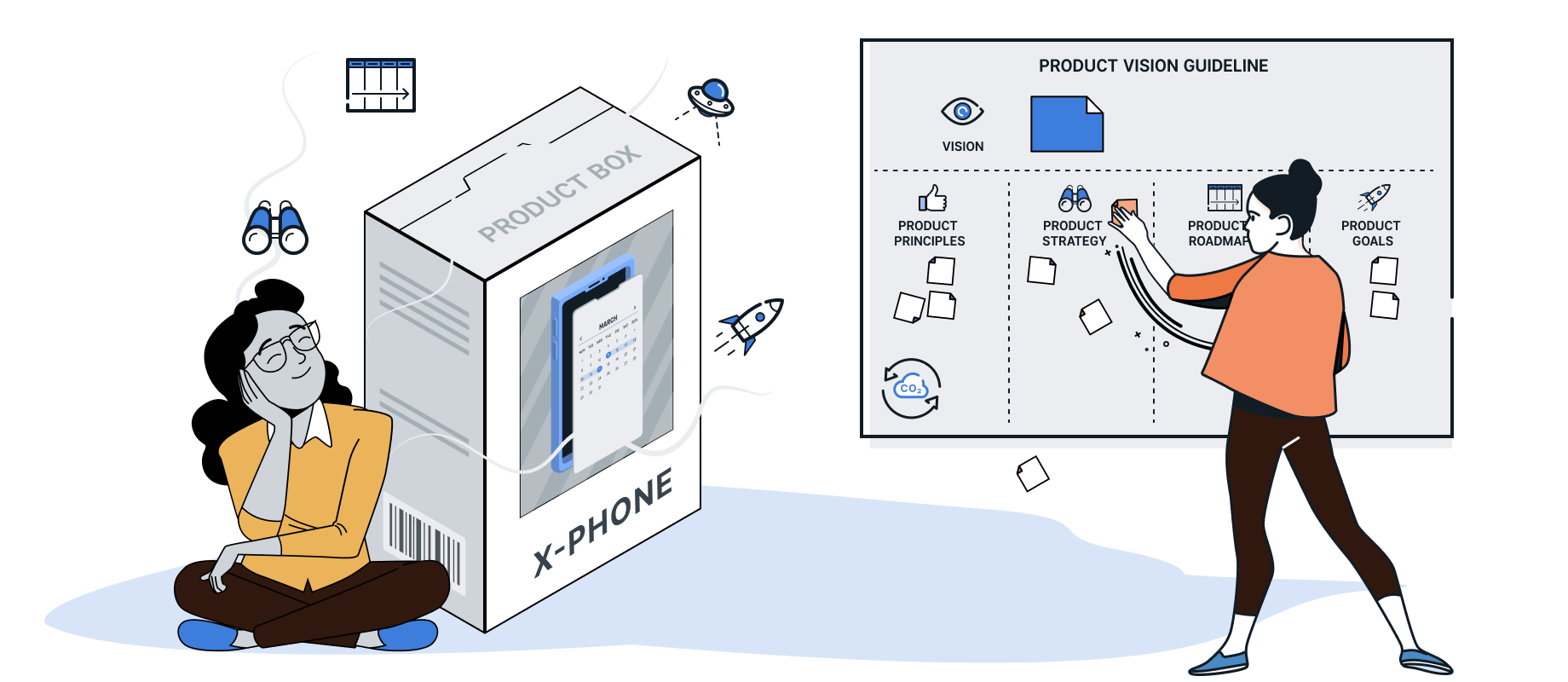
In the following, we will explain in more detail the importance and practical application of product principles, product strategy, product roadmap and product goals for the development and implementation of product visions in agile software projects.
Product principles
Product principles are the fundamental values and beliefs that should underlie every action and decision related to a product. They form the framework that guides the direction and development of the product and ensures that everyone involved pulls in the same direction.
By providing clear guidelines for action, product principles enable consistent and targeted product development. They serve as a point of reference for the entire development team and help to set priorities and make decisions that are in line with the underlying product vision.
Examples of Product Principles:
- "Where possible, we favour the use of sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions."
- This principle illustrates the company's commitment to environmental protection and sustainability and focuses on the development of products that minimise environmental impact.
- "The customers are more important to us than the marketplace partners."
- This principle emphasises the importance of customer orientation and underlines the ambition to develop products that meet the needs and wishes of customers, even if this may lead to conflicts with other partners.
- "Our product is mobile first."
- This principle specifies that the mobile user experience is the top priority in the development of the product. This reflects the importance of mobile technologies today and ensures that the product is optimally tailored to the needs of mobile users.
Product principles form an important basis for successful product development. They clearly define the company's values and beliefs and ensure that these are taken into account at every stage of the product life cycle.
Product strategy
Once the product principles have been defined, the development of a product strategy can begin. The product strategy builds on the previously defined principles and places them in a broader context. It defines the long-term goals, direction and measures required to achieve the desired results and successfully realise the vision.
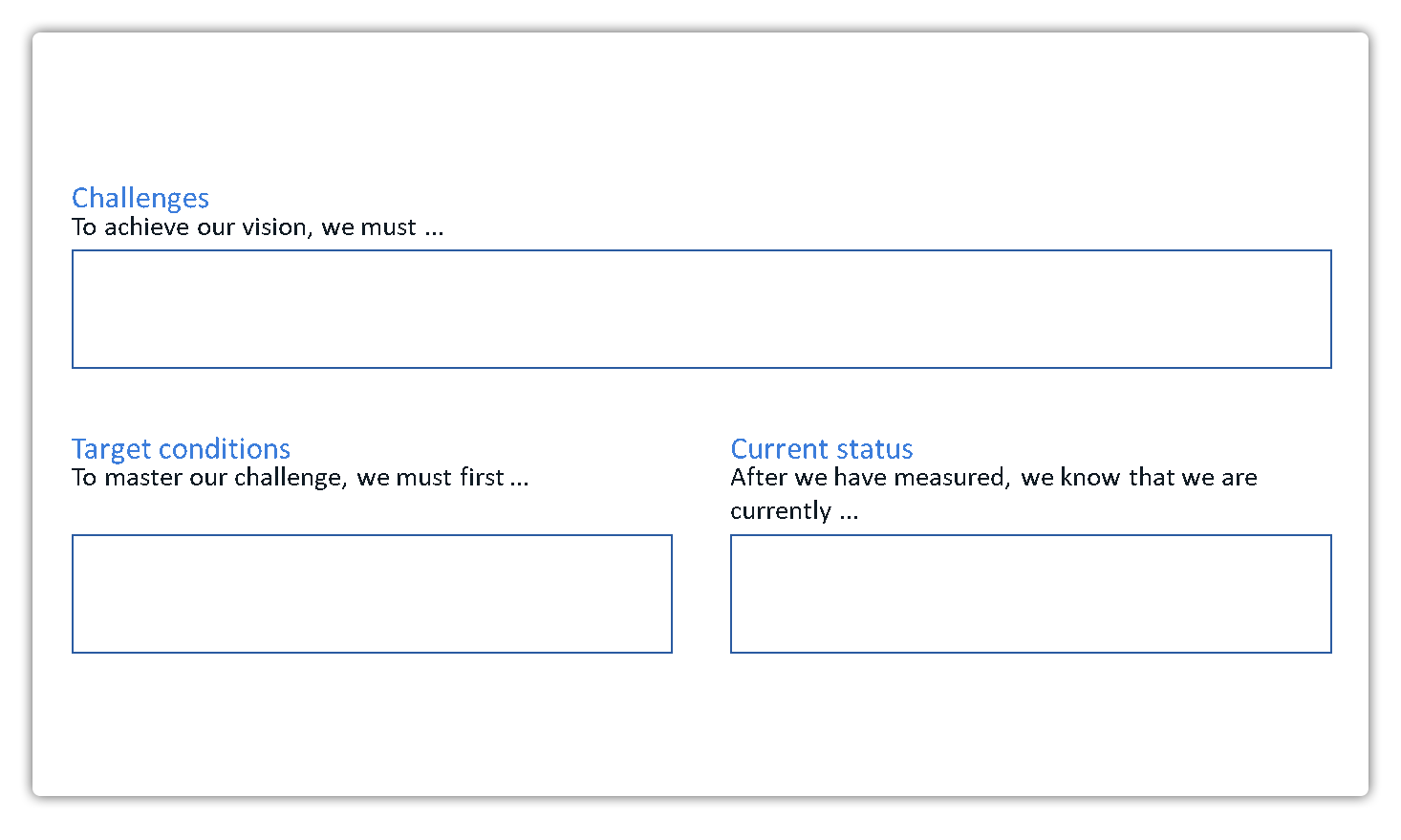
To be effective, a good product strategy should include three essential elements:
-
Diagnosis: This element defines or explains the challenges and obstacles that need to be overcome. It is important to clearly analyse the current situation in order to understand the underlying problems and develop targeted solutions.
-
Mission statement and guidelines: This sets out the values, principles and guidelines by which the development team should proceed. They serve as a framework for dealing with the identified challenges and set the course for product development.
-
Measures: This element comprises a collection of concrete measures that help to fulfil the mission statement and overcome the defined challenges in the best possible way. It includes strategic decisions and activities aimed at realising the product vision and achieving the desired results.
The product strategy is an essential tool for ensuring a clear direction and focus in product development. By integrating the diagnosis, mission statement and guidelines as well as concrete measures, the development team can work effectively towards realising the product vision and respond successfully to challenge

Product roadmap
The product roadmap is essential for identifying the next steps in product development and outlining a strategic roadmap for the development team. It refers to the sequence of topics and ensures that the product vision is reflected in future activities.
A meaningful product roadmap answers important questions and provides clarity for the entire development team:
-
Why is a particular challenge being worked on? The roadmap should clearly communicate the strategic goals and challenges of the product to ensure that all team members understand and work towards the overarching goal.
-
What's next? It shows the next steps and milestones that need to be achieved in order to realise the product vision. This allows the development team to track progress and prioritise.
-
Why is this thing being done first and not another? The roadmap explains the sequence of planned activities and why tasks are prioritised. It helps to allocate resources efficiently and ensure that the most important challenges are dealt with first.
The product roadmap is the guideline for the entire development team and helps to ensure that everyone pulls together to achieve the common goals. It provides orientation, transparency and a clear focus on the product vision, which is essential for the success of a product.
Product goal
The product goal is derived from the product vision and is valid for a period of 6 to 12 months. It describes the specific added value that the product should offer within this period and serves as a reference point for aligning all of the development team's work with it. The focus is on defining the added value and not on the specific implementation of a solution.
A meaningful product goal should be formulated clearly and precisely and make the benefits for users or customers clear. It serves to set the direction for product development and ensure that all activities are aligned with creating this added value.
Examples of product goals:
- "We enable people to check how much electricity they have generated themselves."
- "Our customers can network with others, including in the DACH region."
- "Erik can also take online purchases into account in his consumption analyses."
The examples illustrate how the product goal describes the specific added value that the product should offer without committing to the specific implementation of a solution. It therefore provides a clear direction for the development team and helps to ensure that the work is effectively focussed on achieving the defined goals.
How to start?
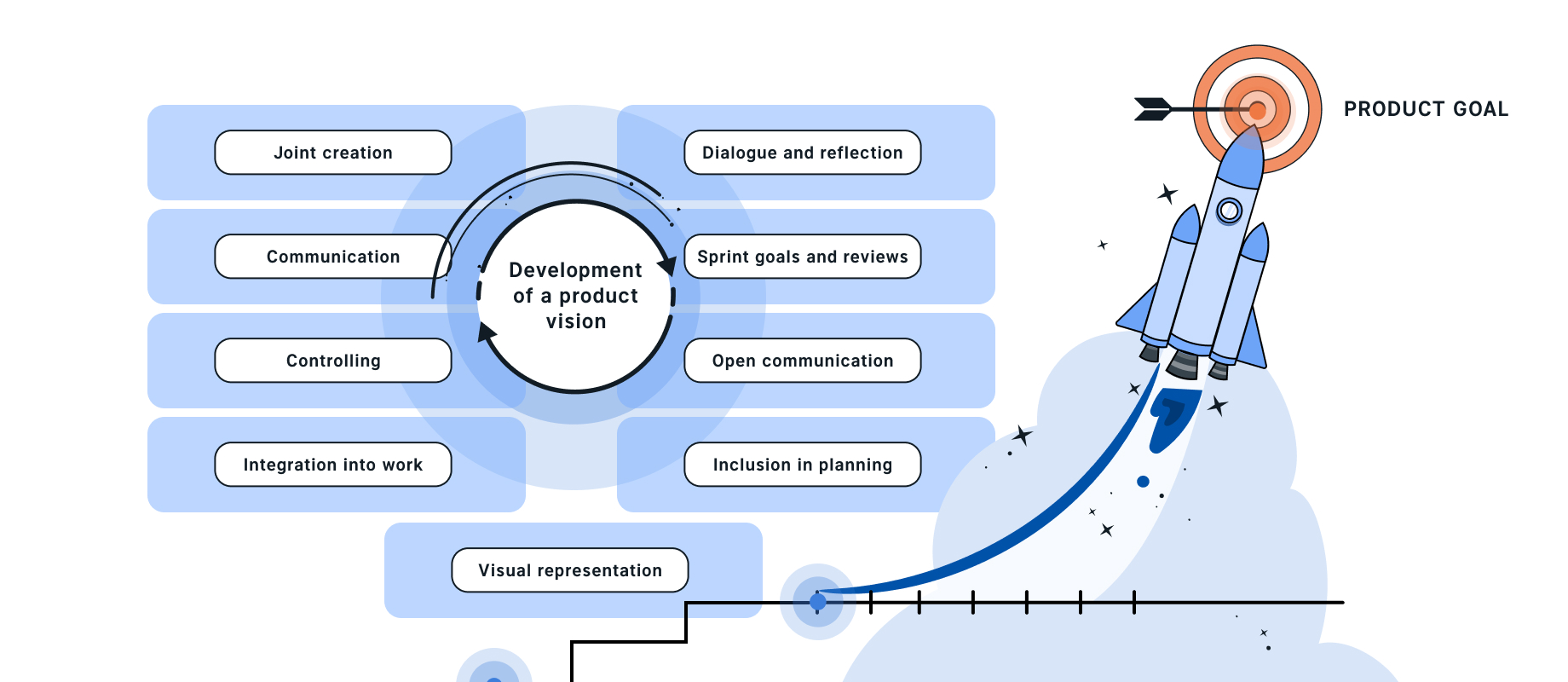
To start developing a product vision, it is essential to follow a structured and participative approach that involves all relevant stakeholders. Here are some steps that can help:
-
Joint creation: The process of developing the product vision should be started together with all those involved. It is important to appoint a person to the role of moderator. This ensures a guided discussion and helps to maintain focus.
-
Communication: The product vision should be shared as often as possible to ensure that everyone is aware of it. Only when communication about the vision feels too frequent are you likely to have reached the right frequency.
-
Controlling: Regular controlling helps to check how well the development team is moving in the direction of the product vision. This allows adjustments to be made and ensures that everyone stays on track.
-
Integration into the work: The vision must be transferred into the strategic and day-to-day work, for example by defining sprint goals that are derived from the product vision or the product goal.
-
Dialogue and reflection: To ensure that all those involved have a common understanding, regular discussions about the vision and a comparison of thoughts on it are essential.
-
Sprint goals and reviews: It is important to formulate sprint goals that are directly derived from the product vision or product goal. Reviews help to reflect on how close you have come to realising the vision.
-
Open communication: Sharing key figures and observations with all stakeholders creates transparency and promotes understanding of progress.
-
Inclusion in planning: To ensure that the product vision serves as a guideline for all decisions and activities, it should be mentioned again at the beginning of every planning process.
-
Visualisation: Visualising the product vision in the team room helps to keep it constantly present and raise awareness of it.
Following these steps ensures that the product vision is clearly defined, understood by everyone and serves as a guideline for the entire product development process. A clear product vision is the key to success in agile software development projects. It creates a common direction and ensures that everyone in the team knows where the journey is heading. Through regular communication and a shared understanding of the vision, teams can work together effectively and set priorities. A product vision is a practical tool that helps to achieve goals and better understand users and customers. Ultimately, it is like a kind of compass that navigates the team through the challenges of software development. It helps to realise software projects that really make a difference.
IT Consulting
Learn more about our services